The Ultimate Guide to the World of Melons
Melons are some of the most popular and diverse fruits available worldwide. From watermelons and cantaloupes to honeydew melons and beyond, there is a melon for every taste and preference. In this article-What is Melon, we will explore the vast world of melons, discuss their benefits, and discover some interesting facts about these refreshing and delicious fruits. Let’s dive in!
Types of Melons
There are countless varieties of melons, each with its unique characteristics, flavors, and textures. Here are some of the most popular types of melons:
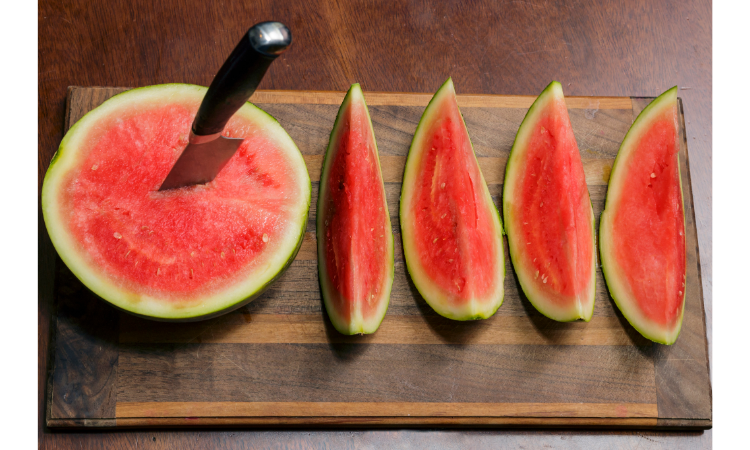
- Watermelon: Watermelon is an iconic summer fruit, known for its juicy, refreshing taste and vibrant red or yellow flesh. Its flesh is typically red or pink, but there are also yellow watermelon varieties. Watermelons are packed with vitamins and minerals and are known for their high water content. Watermelon is high in vitamins A and C and is a great source of hydration, with 92% water content.

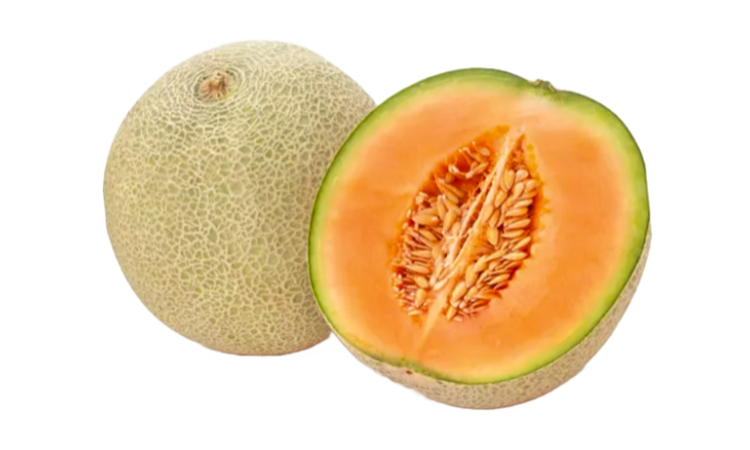
- Cantaloupe: Also known as muskmelon, cantaloupe is a popular melon with sweet, orange flesh. It is an excellent source of vitamins A and C, as well as potassium and fiber. What is cantaloupe juice good for? Cantaloupe juice is a delicious and nutritious beverage that can help keep you hydrated and provide essential vitamins and minerals. It can be enjoyed on its own or mixed with other fruit juices for a refreshing drink.
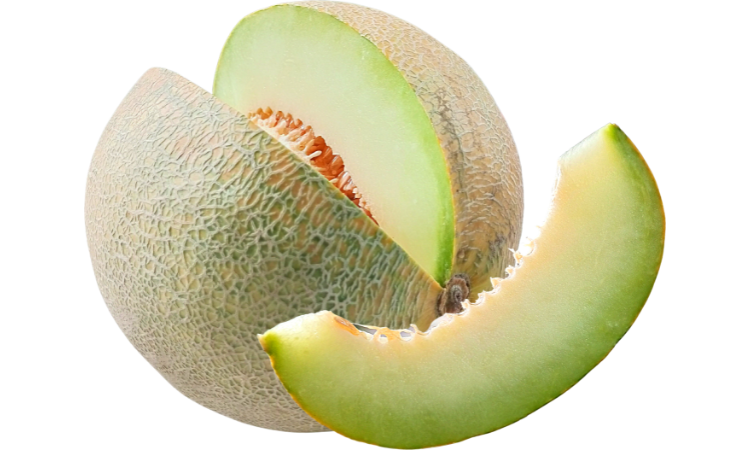
- Honeydew Melon: Honeydew is a green-fleshed melon with a sweet, mild flavor. It is high in vitamins C and K and is often used in fruit salads and smoothies. What is honeydew melon good for? Honeydew melons are delicious on their own, in fruit salads, or as a refreshing addition to smoothies. They can also be paired with prosciutto for a classic Italian appetizer or used in Asian-inspired dishes.

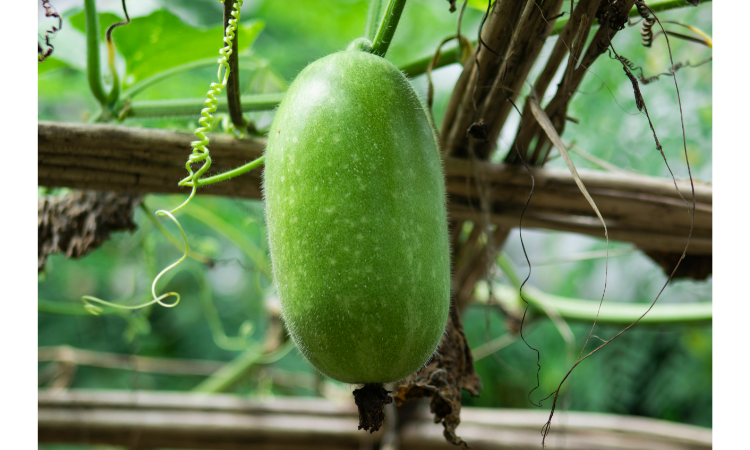
- Winter Melon: Also known as wax gourd, winter melon is a large, green melon with a mild, cucumber-like flavor. It is popular in Asian cuisines and is often used in soups and stir-fries.

- Canary Melon: Canary melon is a bright yellow melon with a sweet, slightly tangy flavor. It is high in vitamins A and C and is often used in fruit salads and desserts.
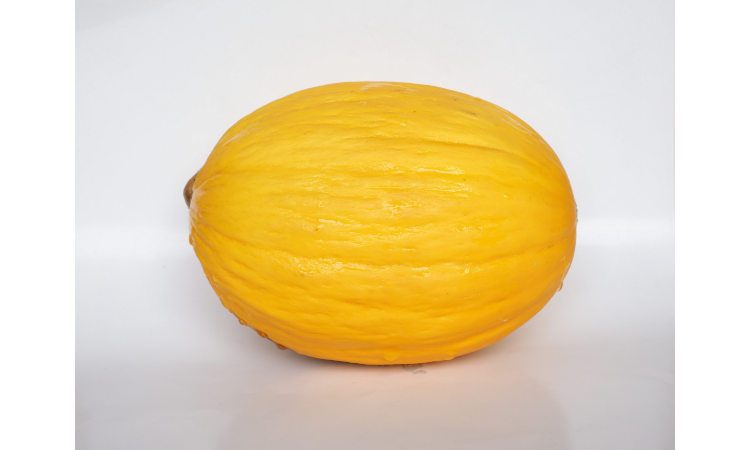

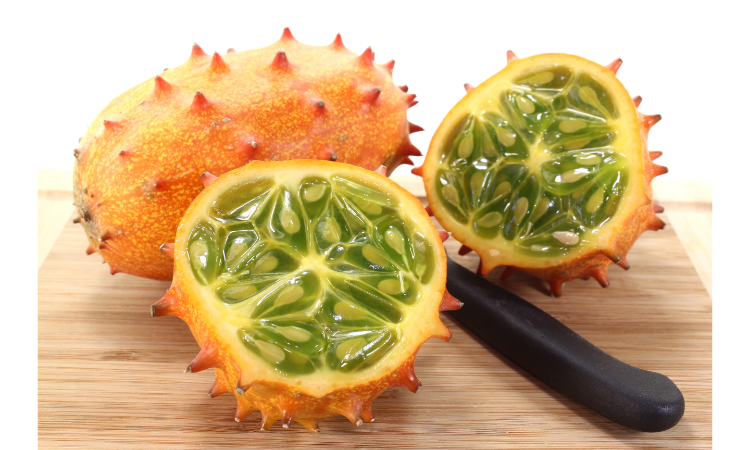
- Kiwano Melon: Kiwano melon, also known as horned melon, has a spiky, orange exterior and a green, jelly-like interior. Its taste is a mix of cucumber, kiwi, and banana.

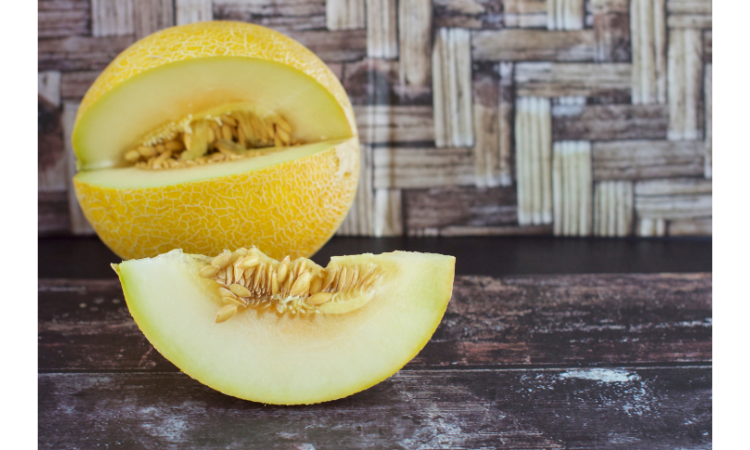
- Galia Melon: Galia melon is a hybrid melon with a sweet, tropical flavor. It has a netted exterior similar to cantaloupe and green, juicy flesh.

What is watermelon sugar?
Watermelon sugar refers to the natural sweetness found in the watermelon and has gained popularity thanks to a catchy song by Harry Styles. The fruit is relatively low in calories, making it a healthy sweet treat.
Health Benefits of Melons

Melons offer a range of health benefits, thanks to their high water content and nutrient-dense composition. Some key benefits include:
- Hydration: Melons have a high water content, making them a refreshing and hydrating snack. For example, watermelon is 92% water, which can help keep you hydrated during hot summer days.
- Antioxidants: Melons are rich in antioxidants like vitamins A and C, which help protect your cells from damage caused by free radicals.
- Digestive health: Many melon varieties contain a good amount of fiber, which promotes healthy digestion and helps prevent constipation.
- Heart health: Melons are a good source of potassium, which helps regulate blood pressure and supports heart health. The watermelon benefits also include the presence of an amino acid called L-citrulline, which can help improve blood flow and lower blood pressure.
- Weight management: Low in calories and high in water content, melons can help you feel full without consuming too many calories. This makes them a great snack option for those looking to maintain or lose weight.
- Immune system support: Vitamin C, found in abundance in many melons, is essential for a healthy immune system. It helps your body produce white blood cells and supports their function in fighting off infections.
How to Select and Store Melons
When choosing a melon at the grocery store or farmer’s market, look for the following characteristics:
- Firmness: Press your thumb gently on the melon’s rind. It should give slightly, but not be too soft. A melon that’s too hard is underripe, while one that’s too soft may be overripe.
- Weight: A ripe melon should feel heavy for its size, which indicates it’s full of water and, therefore, ripe and juicy.
- Aroma: Sniff the stem end of the melon. It should have a pleasant, sweet fragrance.
- Appearance: Look for a melon with a uniform shape and no soft spots, cracks, or dents.
Once you’ve chosen your melon, store it at room temperature until you’re ready to eat it. If you’ve already cut the melon, cover the exposed flesh with plastic wrap and refrigerate it. Cut melon should be consumed within a few days for the best taste and quality.
Ways to Enjoy Melons
Melons are incredibly versatile and can be enjoyed in various ways:
- Raw: Cut melon into wedges, cubes, or balls and eat it as a refreshing snack or add it to a fruit salad.
- Smoothies: Blend melon with other fruits, yogurt, or milk for a delicious and nutritious smoothie.
- Salads: Combine melon with other fruits or vegetables, such as cucumber, mint, and feta cheese, for a light and flavorful salad.
- Grilled: Slice melon and grill it for a few minutes on each side to create a unique and tasty treat. Grilled watermelon, for example, caramelizes and becomes slightly smoky in flavor.
- Desserts: Incorporate melon into sorbets, granitas, or fruit-based desserts for a sweet and refreshing treat.
Interesting Melon Facts
- Melons are part of the Cucurbitaceae family, which also includes cucumbers, squash, and pumpkins.
- Watermelons are 92% water and can weigh up to 200 pounds.
- Melons are believed to have originated in Africa and Asia and were later introduced to Europe by the Romans.
- The world record for the heaviest watermelon is 350.5 pounds, set in 2013 by Chris Kent of Sevierville, Tennessee.
Frequently Asked Questions About Melons
Q: How can I tell if a melon is ripe?
Check for firmness, weight, aroma, and
color. A ripe melon should feel heavy for its size, have a slight give when pressed, and emit a sweet, fragrant aroma. The color of the rind should be even, without any green or overly soft spots.
Q: How should I store melons?
A: Whole, uncut melons can be stored at room temperature for up to a week. Once cut, melons should be wrapped tightly in plastic wrap or stored in an airtight container and refrigerated. They can last up to 3-4 days in the refrigerator.
Q: Can I freeze melons?
A: Yes, melons can be frozen, but their texture will change slightly when thawed. To freeze melons, cut them into cubes or balls and arrange them in a single layer on a baking sheet. Freeze until solid, then transfer to an airtight container or freezer bag. Frozen melons can be used in smoothies, sorbets, or as a cool treat on their own.
Q: Are melon seeds edible?
A: Yes, melon seeds are edible and can be roasted for a crunchy snack. To roast melon seeds, rinse and dry them thoroughly, then spread them out on a baking sheet. Season with salt or other desired spices and bake at 325°F (163°C) for 10-15 minutes, or until golden brown and crispy.
Q: Are melons safe to eat for people with diabetes?
A: While melons do contain natural sugars, they have a relatively low glycemic index, which means they don’t cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. People with diabetes can enjoy melons in moderation, as part of a balanced diet. However, it’s essential to monitor individual blood sugar responses and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Q: What is the difference between a melon and a gourd?
A: Melons and gourds are both members of the Cucurbitaceae family, but they belong to different genera. Melons are part of the Cucumis genus, while gourds belong to the Lagenaria or Cucurbita genera. Melons are typically sweet and consumed as fruits, whereas gourds are usually more bitter or bland and used as vegetables. Gourds often have a harder rind and are more commonly used for decorative or utilitarian purposes, such as making containers or musical instruments.
Q: How do I know when my melon plants are ready for harvest?
A: The ideal time to harvest melons varies depending on the type of melon. In general, signs that a melon is ready for harvest include:
- A sweet, fragrant aroma at the blossom end of the fruit
- A change in rind color, such as a yellowing of the skin for cantaloupe and honeydew melons
- A slight softening at the blossom end of the fruit
- The fruit detaches easily from the vine with a gentle tug or twist (slip stage)
Keep in mind that these signs may vary slightly depending on the specific variety of melon, so consult the seed packet or growing instructions for more precise guidelines.
Q: Can I grow melons in containers?
A: Yes, melons can be grown in containers, but it’s essential to choose a suitable variety and provide adequate growing conditions. Select a dwarf or bush variety of melon that is well-suited to container gardening. The container should be large enough to accommodate the plant’s root system (at least 18-24 inches in diameter) and have drainage holes. Use a high-quality potting mix, and ensure the plant receives plenty of sunlight, water, and nutrients. Providing a trellis for the melon vines to climb can help save space and keep the fruit off the ground.
Q: Can melons cross-pollinate?
A: Melons can cross-pollinate, but only within their own species. This means that different varieties of the same species (e.g., cantaloupe and honeydew) can cross-pollinate, potentially resulting in hybrid seeds with mixed characteristics. However, melons will not cross-pollinate with other species of melons, such as watermelons. To prevent cross-pollination, grow melon varieties of the same species at least 800 feet apart or use physical barriers like row covers to protect the plants during flowering.
Q: What is Melona?
Melona is a popular South Korean ice cream bar made from melon-flavored cream. The ice cream bars are known for their smooth and creamy texture and are available in various flavors, including the original melon, as well as strawberry, banana, and mango.
Q: Melon 24 Hits
Melon 24 Hits refers to a playlist that features the top 24 songs on Melon, which is a South Korean online music store and streaming service. The playlist is updated regularly to reflect the most popular tracks among users.
Q: What is Melon Bread?
Melon bread, or melon pan, is a type of Japanese sweet bread. The bread gets its name from its appearance, which resembles the outer skin of a melon. Melon bread is made from a soft and fluffy dough covered with a thin layer of cookie dough that becomes crisp when baked, giving the bread its distinctive melon-like texture. Despite its name, melon bread does not typically contain any melon flavoring.
Q: What is Watermelon High In?
Watermelon is high in several essential nutrients and vitamins, including vitamin C, vitamin A, and potassium. It is also an excellent source of lycopene, a powerful antioxidant known for its potential health benefits, such as reducing the risk of heart disease and some types of cancer. Additionally, watermelon is made up of 92% water, making it a hydrating and low-calorie snack.
Q: What is Melon Liqueur?
Melon liqueur, also known as Midori, is a sweet and fruity alcoholic beverage made from muskmelons. With its vibrant green color and distinctive melon flavor, it is commonly used in cocktails, such as the Midori Sour, Melon Ball, and Japanese Slipper.
Q: What is a Melon Baller?
A melon baller is a kitchen utensil designed to scoop out small, round balls of melon flesh. It typically features a small, round, metal scoop on one or both ends of a handle. Melon ballers are often used to create visually appealing fruit salads or garnishes.
Q: What is Bitter Melon Used For?
Bitter melon, also known as bitter gourd or karela, is a tropical and subtropical vine from the Cucurbitaceae family. It is often used in traditional medicine for its potential health benefits, such as improving blood sugar levels, boosting immunity, and aiding in digestion. Bitter melon is also a popular ingredient in various cuisines, particularly in Asian dishes, where its distinct bitter flavor is valued.
With so many varieties and ways to enjoy them, melons are a delicious and nutritious addition to your summer menu. Dive into the world of melons and discover your favorite way to savor their juicy goodness!
