Eggplant, known in some parts as aubergine, is more than just a key ingredient in moussaka or a baba ghanoush dish. About eggplant, this vibrant, purple vegetable boasts an array of health benefits that can significantly impact one’s overall well-being. From promoting heart health to enhancing bone health, the humble eggplant has plenty to offer. Let’s dive deep into the health benefits of eggplant, and its nutritional profile and explore the numerous advantages of incorporating it into your diet.
Eggplant Nutrition Facts

When we talk about the health benefits of eggplant, it’s essential first to understand its nutritional makeup. Rich in vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber, the eggplant is a nutrient powerhouse. Here are some key points:
- Vitamin C & B6: Important for skin health and neurological function.
- Potassium: Essential for heart health.
- Dietary fiber: Aids in digestion and helps control blood sugar levels.
- Folate: Helps in DNA synthesis and prevents birth defects.
It’s not just about the vitamins and minerals. Eggplants also contain anthocyanins, which are antioxidants that help protect cells from damage.
The Best Way to Prepare Eggplant
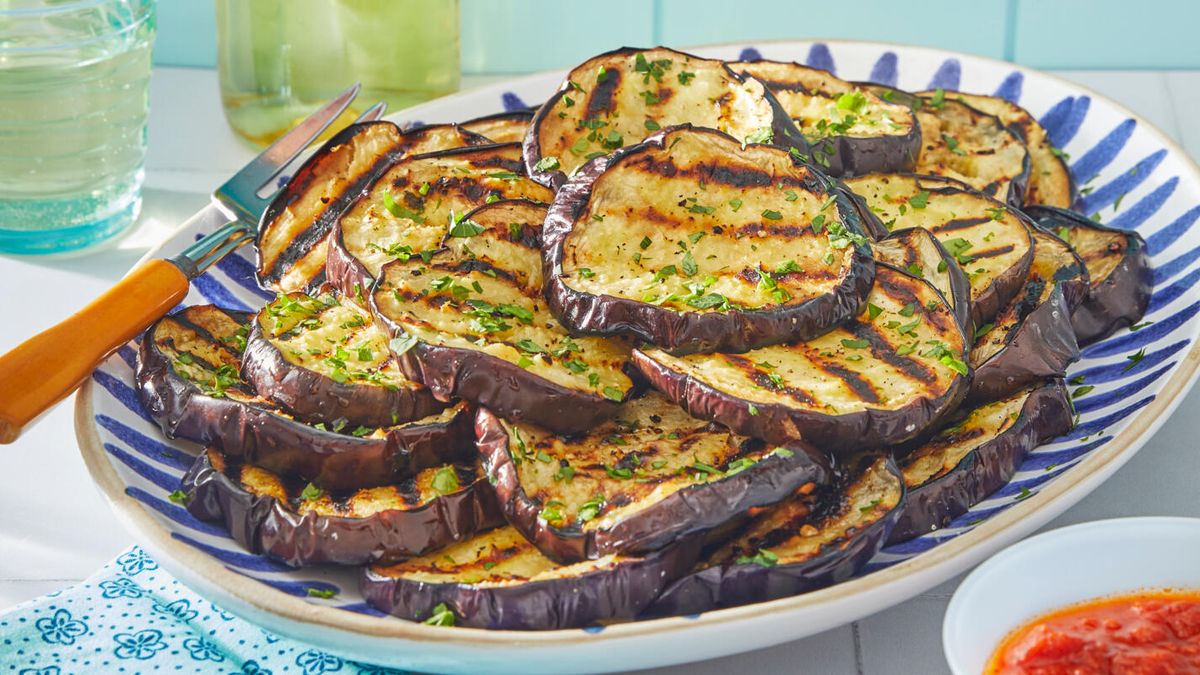

Before delving into the benefits, let’s talk about how to maximize the goodness of eggplants through preparation. The preparation can impact not just taste, but nutritional value as well.
- Grilling or Baking: This method retains most of its nutrients. A simple drizzle of olive oil with a sprinkle of salt and pepper can make a delicious dish.
- Steaming: Helps in retaining the vegetable’s antioxidants.
- Stir-Frying: Quick and uses less oil, ensuring you don’t lose many nutrients.
Avoid excessive frying, as it may reduce the nutritional value and increase calorie intake.
Exploring the Health Benefits of Eggplant
With its dense nutritional profile, eggplant offers a plethora of health benefits:
Promote Heart Health

The fiber, potassium, and vitamin C in eggplants are all beneficial for heart health. Anthocyanins, a type of antioxidant, have been linked to reduced blood pressure and lower risk of heart attacks.
Control Blood Sugar Levels
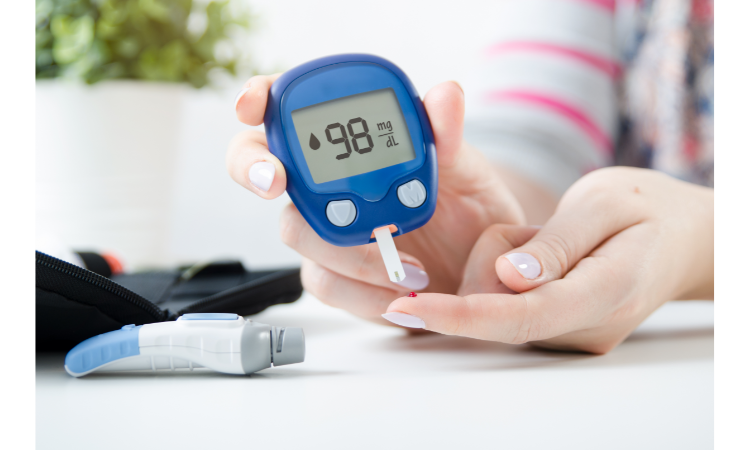

The fiber and polyphenols in eggplants can help control blood sugar levels, making it beneficial for those with diabetes.
Improve Cognitive Function
Nasunin, an antioxidant in the eggplant’s skin, can protect brain cell membranes from damage, aiding cognitive function.
Reduce Cancer Risk

Polyphenols in eggplants can have anti-cancer effects, inhibiting the growth of tumors and the spread of cancer cells.
Help in Weight Loss

Being low in calories and rich in fiber, eggplants can promote satiety and reduce overall calorie intake.
Enhance Bone Health
The presence of vitamin K and calcium makes eggplants beneficial for bone health, reducing the risk of bone fractures.
Promote Eye Health

Eggplants contain lutein, which is beneficial for eye health, reducing the risk of cataracts and age-related macular degeneration.
Improve Skin Health

The antioxidants and vitamins in eggplants can protect the skin from ultraviolet radiation and free radicals.
Help Treat Anemia
The iron and copper in eggplants can help in the formation of red blood cells, addressing conditions like anemia.
Prevent Birth Defects
Folate in eggplants ensures healthy fetal development, preventing congenital disabilities.
Tips for Selecting and Storing Eggplant

To make the most of the health benefits of eggplant, it’s crucial to select the freshest produce and store it appropriately.
Selecting Eggplant
When picking out eggplants from your local market or store:
Texture: The skin should be smooth and shiny, free from any blemishes or discolorations.
Firmness: Give it a gentle squeeze. A fresh eggplant will be slightly firm but will give under pressure.
Size: Opt for medium-sized eggplants. Overly large ones might be bitter and have tougher seeds.
Weight: It should feel heavy for its size, indicating that it’s full of moisture.
Stem: The stem should be bright green, signifying freshness.
Storing Eggplant
Once you bring the eggplant home:
Do Not Refrigerate: If you plan to use the eggplant within a couple of days, it’s best to store it at room temperature.
Avoid Moisture: If storing in the refrigerator, keep it in the produce drawer away from fruits to avoid moisture, which can make it rot quickly.
Use Quickly: Eggplant is best consumed within a few days of purchase to ensure you’re getting the maximum nutrients and taste.
Eggplant: A Beacon for Future Agriculture

In an era where climate change is altering farming patterns and challenging traditional agricultural practices, the eggplant emerges as a beacon of hope. Its resilient nature and adaptability are setting an example for sustainable agriculture.
Eggplant and Climate Resilience
Eggplant’s ability to grow in varied climates, from the hot plains of Asia to the temperate zones of Europe, makes it a crop of choice for future-proofing agriculture:
- Drought Resistance: Eggplants require relatively less water compared to other crops, making them suitable for regions facing water scarcity.
- Pest Resistance: Certain varieties of eggplants have shown resistance to common pests, reducing the need for chemical interventions.
- Soil Versatility: From sandy to loamy, eggplants can thrive in a range of soil types, offering flexibility for farming.
Innovations in Eggplant Cultivation
As the world recognizes the potential of eggplants, both in terms of health benefits and sustainability, there’s a surge in innovative cultivation techniques:
Hydroponic Farming: Growing eggplants without soil, using nutrient-rich water solutions, ensures higher yields and quality.
Vertical Farming: In urban environments, where space is at a premium, vertical farming of eggplants is being explored.
Genetic Modification: Scientists are researching ways to enhance the nutritional profile of eggplants and improve their resistance to pests and diseases.
Potential Risks and Considerations

As we’ve touched upon the vast health benefits of eggplant, it’s also essential to consider a few points:
Allergies: Some individuals might be allergic to eggplants, causing reactions like itching, hives, or even more severe symptoms.
Oxalates: Eggplants contain oxalates, which can crystallize and cause health issues for individuals with kidney or gallbladder problems.
Solanine: Found in the green parts of the eggplant, solanine can be toxic if consumed in large amounts. Always trim the green parts before consumption.
In Conclusion
The health benefits of eggplant are undeniable. Packed with essential nutrients and offering a myriad of advantages, it is an excellent addition to any diet. From protecting the heart to supporting cognitive function, eggplants prove to be a versatile and beneficial vegetable.
So the next time you’re looking to prepare a healthy meal, remember to include eggplants. Not only will you enjoy a delightful dish, but your body will thank you for all the health benefits it brings.
